Two, three-channel detector systems, shipped to Hefei, China for use at the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST)
Proposal for an experimental superconducting magnetic fusion energy tokamak to be built at Hefei was made in 1996, and construction of the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak was completed in March 2006. The Institute of Plasma Physics through the Chinese Academy of Sciences are responsible for the tokamak.
During September 2006 plasma discharge was successfully acheived in EAST. To probe the conditions of the plasma, a Deuterium Carbon Nitrogen (DCN) interferometer working at far infrared / mm wave frequencies and coupled with a suitable detector, is used to measure plasma electron line density.
Initial testing with an Indium Antimonide (InSb) detector showed a sensitivity improvement over the existing Triglycine Sulphate (TGS) pyroelectric detectors, hence QMC Instruments Ltd., was asked to provide two multi-channel InSb detector systems for EAST to operate at an optical wavelength of 195um and a speed of 10kHz.

One of the 3-channel downward looking detector systems. Three dual channel
Type ULN95/2 preamplifiers are attached to the sides of the detector system
Two downward-looking InSb hot electron bolometers with magnetically enhanced response were designed and built. A uniform 0.75T magnetic field provided the 1.54THz peak frequency response for each detector. Three detectors were mounted into each cryostat.

View inside the detector system showing the three downward looking detectors
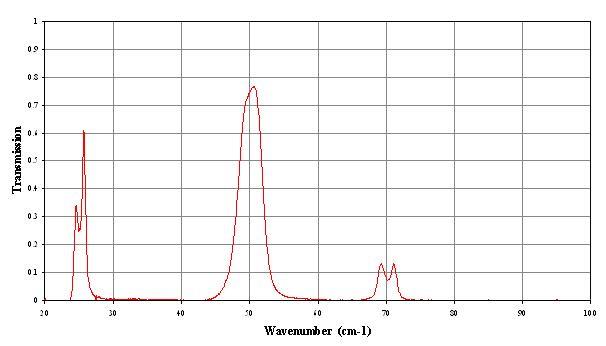
A 200um band-pass filter (profile below), suited to the observation wavelength, is mounted at 4.2K - one for each detector.
Edited Sep09